Loading challenge...
Preparing the challenge details...
Loading challenge...
Preparing the challenge details...
Create an animated dice roller component in React with realistic rolling animations, random number generation, multiple dice support, and roll history tracking.
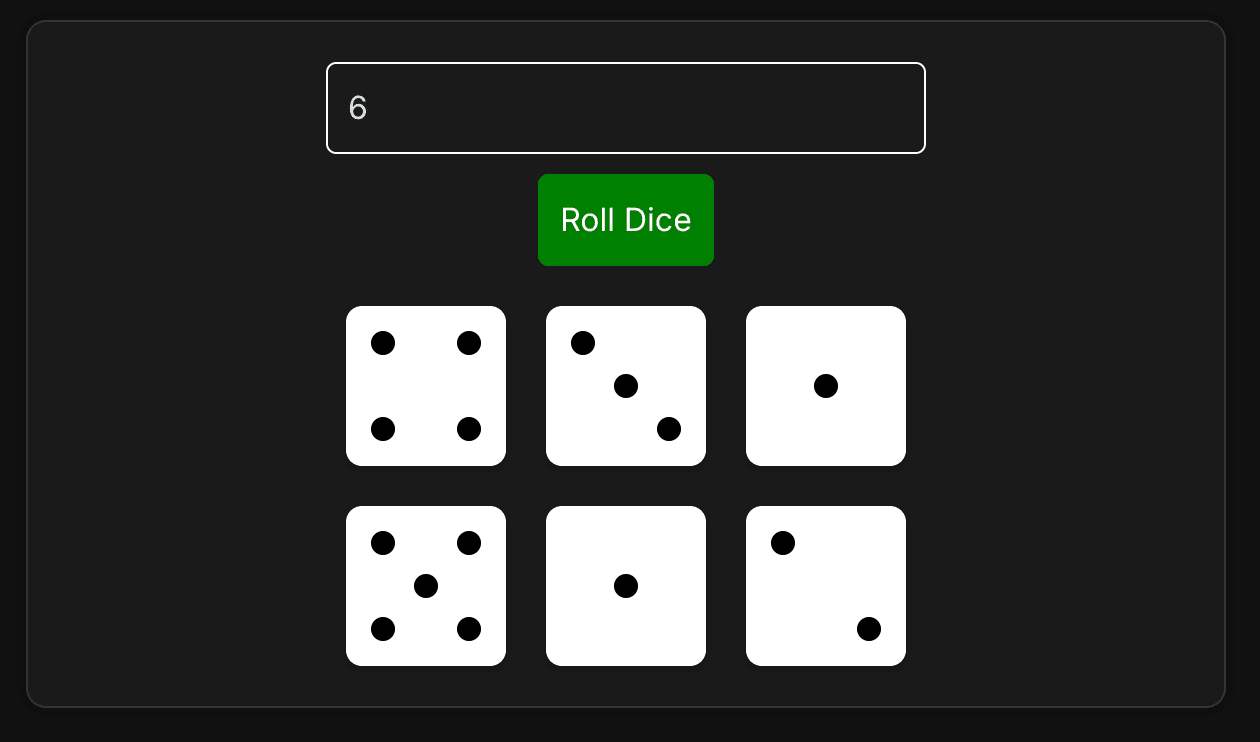
Build a dice roller component that displays multiple dice with accurate dot patterns. The key challenges are generating random dice values, mapping numbers to visual dot patterns, and using CSS Grid to position dots correctly on each die face.
A dice roller allows users to specify how many dice to roll (1-12) and displays each die with the correct number of dots arranged in the standard pattern. Each die face shows dots in a 3×3 grid layout, matching real-world dice patterns.
The most critical part is mapping each dice value (1-6) to its corresponding dot positions. Standard dice follow specific patterns that must be accurately represented.
Each die face uses a 3×3 grid where dots can be placed. Here are the patterns:
1 dot (center):
┌───┬───┬───┐
│ │ │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ ● │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ │ │
└───┴───┴───┘
2 dots (diagonal):
┌───┬───┬───┐
│ ● │ │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ │ ● │
└───┴───┴───┘
3 dots (diagonal):
┌───┬───┬───┐
│ ● │ │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ ● │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ │ ● │
└───┴───┴───┘
4 dots (corners):
┌───┬───┬───┐
│ ● │ │ ● │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ ● │ │ ● │
└───┴───┴───┘
5 dots (corners + center):
┌───┬───┬───┐
│ ● │ │ ● │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ │ ● │ │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ ● │ │ ● │
└───┴───┴───┘
6 dots (two columns):
┌───┬───┬───┐
│ ● │ │ ● │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ ● │ │ ● │
├───┼───┼───┤
│ ● │ │ ● │
└───┴───┴───┘
We use a lookup object to map each value to its dot positions:
TSXcomponent.tsx1const getDotPositions = (value: number): string[] => { 2 const positions: Record<number, string[]> = { 3 1: ['center'], 4 2: ['top-left', 'bottom-right'], 5 3: ['top-left', 'center', 'bottom-right'], 6 4: ['top-left', 'top-right', 'bottom-left', 'bottom-right'], 7 5: ['top-left', 'top-right', 'center', 'bottom-left', 'bottom-right'], 8 6: ['top-left', 'top-right', 'middle-left', 'middle-right', 'bottom-left', 'bottom-right'] 9 }; 10 return positions[value] || []; 11};
Key Points:
Generating random dice values uses Math.random() and Math.floor():
TSXcomponent.tsx1function rollDice(count: number) { 2 return Array.from({ length: count }, () => Math.floor(Math.random() * 6) + 1); 3}
How it works:
Math.random() generates a number between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (exclusive)Math.floor() rounds down to integers 0-5Example:
Math.random() = 0.73 → 0.73 × 6 = 4.38 → Math.floor(4.38) = 4 → 4 + 1 = 5Math.random() = 0.15 → 0.15 × 6 = 0.9 → Math.floor(0.9) = 0 → 0 + 1 = 1The implementation follows a parent-child component pattern:
Manages the application state and user interaction:
TSXcomponent.tsx1const DiceRoller = () => { 2 const [numberOfDice, setNumberOfDice] = useState<string>(''); 3 const [results, setResults] = useState<number[]>([]); 4 5 function handleRollDice() { 6 const count = Number(numberOfDice); 7 if (isNaN(count) || count < 1 || count > 12) { 8 return; 9 } 10 const rolled = rollDice(count); 11 setResults(rolled); 12 } 13 14 return ( 15 <div className="dice-roller-container"> 16 <input 17 type="number" 18 value={numberOfDice} 19 onChange={(e) => setNumberOfDice(e.target.value)} 20 /> 21 <button onClick={handleRollDice}>Roll Dice</button> 22 {results.length > 0 && <DiceRollerComponent results={results} />} 23 </div> 24 ); 25};
Responsibilities:
State Management:
numberOfDice: String to allow empty input (better UX)results: Array of dice values (1-6) to displayRenders the visual dice faces:
TSXcomponent.tsx1const DiceRollerComponent = ({ results }: { results: number[] }) => { 2 return ( 3 <div className="dice-roller"> 4 {results.map((result, index) => { 5 const dotPositions = getDotPositions(result); 6 return ( 7 <div key={index} className="dice-face"> 8 {dotPositions.map((position, dotIndex) => ( 9 <span key={dotIndex} className={`dot ${position}`}></span> 10 ))} 11 </div> 12 ); 13 })} 14 </div> 15 ); 16};
Responsibilities:
Each die face uses a 3×3 CSS Grid to position dots accurately:
CSSstyles.css1.dice-face { 2 width: 80px; 3 height: 80px; 4 background-color: white; 5 border-radius: 8px; 6 display: grid; 7 grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr); 8 grid-template-rows: repeat(3, 1fr); 9 padding: 8px; 10}
Grid Structure:
┌─────┬─────┬─────┐
│ 1 │ 2 │ 3 │ Row 1
├─────┼─────┼─────┤
│ 4 │ 5 │ 6 │ Row 2
├─────┼─────┼─────┤
│ 7 │ 8 │ 9 │ Row 3
└─────┴─────┴─────┘
Each dot position maps to a specific grid cell:
CSSstyles.css1.dot.center { 2 grid-column: 2; 3 grid-row: 2; 4} 5 6.dot.top-left { 7 grid-column: 1; 8 grid-row: 1; 9} 10 11.dot.top-right { 12 grid-column: 3; 13 grid-row: 1; 14} 15 16.dot.middle-left { 17 grid-column: 1; 18 grid-row: 2; 19} 20 21.dot.middle-right { 22 grid-column: 3; 23 grid-row: 2; 24} 25 26.dot.bottom-left { 27 grid-column: 1; 28 grid-row: 3; 29} 30 31.dot.bottom-right { 32 grid-column: 3; 33 grid-row: 3; 34}
Why CSS Grid?
The component validates user input before rolling:
TSXcomponent.tsx1function handleRollDice() { 2 const count = Number(numberOfDice); 3 if (isNaN(count) || count < 1 || count > 12) { 4 return; // Invalid input, do nothing 5 } 6 const rolled = rollDice(count); 7 setResults(rolled); 8}
Validation Checks:
isNaN(count): Ensures input is a valid numbercount < 1: Prevents rolling zero or negative dicecount > 12: Limits to reasonable maximum (prevents performance issues)Why String State for Input?
Using useState<string>('') instead of useState<number>(0) allows:
The component uses a responsive grid to display multiple dice:
CSSstyles.css1.dice-roller { 2 display: grid; 3 grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fill, minmax(80px, 1fr)); 4 gap: 20px; 5 max-width: 600px; 6 width: 100%; 7}
Features:
auto-fill: Automatically creates columns based on available spaceminmax(80px, 1fr): Each die is at least 80px wide, can grow to fill spaceMath.floor(Math.random() * 6) + 1 generates values 1-6auto-fill for flexible layoutsThe beauty of this approach is its simplicity and accuracy. The pattern mapping ensures each die looks correct, and CSS Grid handles all the positioning automatically. Whether rolling 1 die or 12, the same logic works perfectly.
Goal: Implement a dice roller component that can be used to roll dice.
Continue learning with these related challenges

Create an interactive image carousel in React with smooth slide transitions, navigation arrows, dot indicators, autoplay, and touch/swipe support for mobile devices.

Build a dynamic Tic Tac Toe game in React with customizable grid sizes, win detection algorithms, player turn management, and game reset functionality. Great for interviews.

Build a fun Whack-a-Mole game in React with random mole spawning, click detection, score tracking, countdown timer, and increasing difficulty levels. Perfect for React practice.

Create an interactive image carousel in React with smooth slide transitions, navigation arrows, dot indicators, autoplay, and touch/swipe support for mobile devices.

Build a dynamic Tic Tac Toe game in React with customizable grid sizes, win detection algorithms, player turn management, and game reset functionality. Great for interviews.

Build a fun Whack-a-Mole game in React with random mole spawning, click detection, score tracking, countdown timer, and increasing difficulty levels. Perfect for React practice.